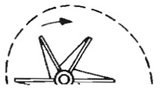
- BI – Backward Incline
The tips of the blades are inclined away from the direction of rotation. Used in commercia-industrial, heavy-duty heating and cooling systems that require heavy-duty construction, non-overloading characteristics and stable air delivery. These blowers operate at higher efficiencies than forward curved blowers. Not as quiet as forward curve blowers because they operate at higher speeds. Can be used in systems up to 3″ static pressure. Smaller diameter wheels are supplied with flat blades; larger diameter wheels are supplied with air foil blades to improve efficiency.
- BTU – British Thermal Unit
The amount of energy or heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water one degree Fahrenheit. - CFM – Cubic Feet Per Minute
A measure of volume flow rate, or air moving capability, of an air moving device. Volume of air moved per minute. - dB – Decibel
A measure of the sound produced by an air moving device. - FC – Forward Curve
The tips of the blades are inclined in the direction of rotation; the most common type of centrifugal blower. Normally used in residential heating and air conditioning systems and light-duty exhaust systems where maximum air delivery and low noise levels are required. Capable of pressures up to approximately 1’/2″ SP.
- Radial Blade
Has straight blades that are, to a large extent, self-cleaning, making them suitable for various kinds of material handling and particle-and-grease laden air. Wheels are of simple construction and have relatively narrow blades. They can withstand the high speeds required to operate at higher static pressures (up to 12″) but usually are noisier than FC or BI blowers.
- Sone
An internationally recognized unit of loudness. Sones signify, in a single number, the total sound output of the unit being tested. One sone is approximately equal to the sound of a modern refrigerator in a kitchen. A 6-sone fan, for example, sounds twice as loud to the human ear as a 3-sone fan. - SP – Static Pressure
A measure of the resistance to movement of forced air through a system or installation, caused by ductwork, inlets, louvers, etc. Measured in inches of water gauge (W.G.); the height, in inches, to which the pressure will lift a column of water. For a given system, static pressure varies as the square of the flow rate. Thus, if flow rate is doubled, system resistance or static pressure is increased four times.